Jun 29, 2020
Nanotechnology applied to medicine: The first liquid retina prosthesis
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: biotech/medical, cyborgs, evolution, life extension, nanotechnology
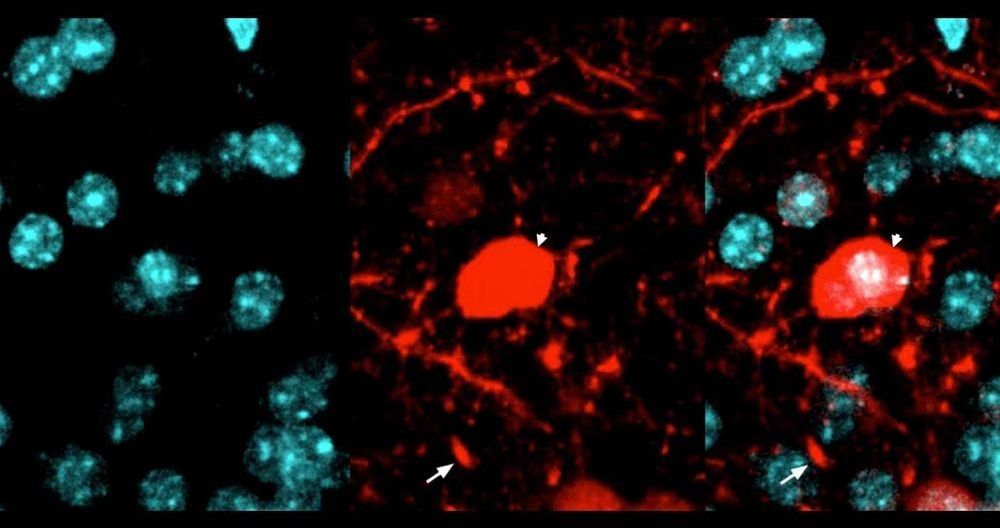
Research at IIT-Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (Italian Institute of Technology) has led to the revolutionary development of an artificial liquid retinal prosthesis to counteract the effects of diseases such as retinitis pigmentosa and age-related macular degeneration that cause the progressive degeneration of photoreceptors of the retina, resulting in blindness. The study has been published in Nature Nanotechnology.
The study represents the state of the art in retinal prosthetics and is an evolution of the planar artificial retinal model developed by the same team in 2017 and based on organic semiconductor materials (Nature Materials 2017, 16: 681–689).
The ‘second generation’ artificial retina is biomimetic, offers high spatial resolution and consists of an aqueous component in which photoactive polymeric nanoparticles (whose size is 350 nanometres, thus about 1/100 of the diameter of a hair) are suspended, and will replace damaged photoreceptors.