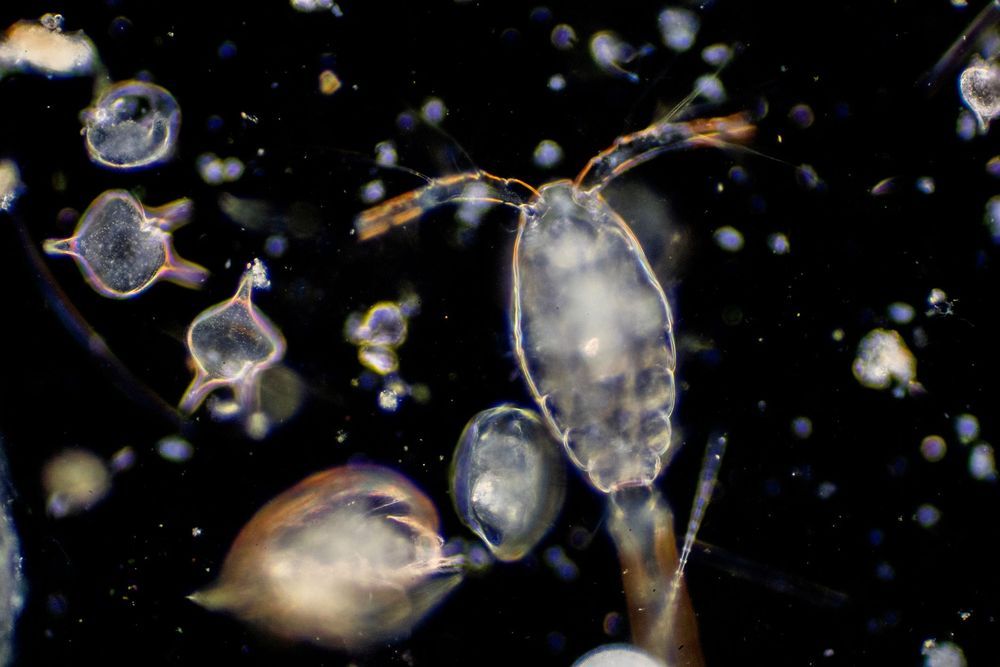
While satellite imaging lets researchers observe the outer life of plankton populations, the complex genetics in microscopic marine life have made looking inward more challenging. According to a new study published in Nature Methods, researchers from the University of East Anglia were able to deliver and express foreign DNA in 13 species that have never before transformed. They were also able to evaluate the potential cause of non-transformation in 17 other species; in turn, laying the foundation for an expanded understanding of genomes discovered in plankton.
The sheer variety of plankton potential — from antibacterial compounds to antiviral and antifungal solutions — makes this a worthwhile endeavor. If scientists can create reliable methods to modify phytoplankton, it should be possible to reduce their toxic impact, better control their bloom cycle and even increase the photosynthetic output — all critical in the fight to keep our oceans blue and our terra firma green.
As noted by Science Magainze, the international research team used a variety of methods to modify plankton DNA. For some species, shooting tiny gold or tungsten particles covered with DNA through cell walls produced the best result. For others, jolts of electricity made cell walls “leaky” and allowed new DNA to seep through. Specific protist successes included modification of a fish-killing toxic plankton species, and one that infects both mollusks and amphibians. While these discoveries don’t present a complete understanding of the genetics in microscopic marine life, they provide a key testing protocol: By modifying genetic structure and then observing how plankton react, teams could uncover ways to boost antibiotic resistance or lower infectious impact. According to lead UK study author Thomas Mock, “These insights will improve our understanding about their role in the oceans, and they are invaluable for biotechnological applications such as building factories for biofuel or the production of bioactive compounds.”