Archive for the ‘biological’ category: Page 194
Dec 15, 2017
Bioquark Inc. — Happy and Healthy Over 40 Podcast
Posted by Ira S. Pastor in categories: aging, bioengineering, biological, biotech/medical, cryonics, disruptive technology, health, life extension, posthumanism, transhumanism
http://happyandhealthyover40.com/relieving-suffering-emerging-bio-technology/
http://happyandhealthyover40.com/relieving-suffering-emerging-bio-technology/
Tags: anti-aging, biotech, biotechnology, health, healthspan, immortality, longevity
Dec 6, 2017
Is quantum artificial life possible?
Posted by Alexander Rodionov in categories: biological, computing, quantum physics
Yes.
Physicists in the QUTIS Quantum Biomimetics and Quantum Artificial Life research group at the Department of Physical Chemistry, University of the Basque Country in Spain have harnessed the unprecedented power of the IBM Q Cloud Quantum Computer —recently made available for public use ( IBM makes 20 qubit quantum computing machine available as a cloud service) —to reproduce the hallmark features of Darwinian life and evolution in microscopic quantum systems, proving they can efficiently encode quantum features and biological behaviors that are usually associated with living systems and natural selection.
Dec 2, 2017
Aging Expert: The First Person to Live to 1,000 Has Already Been Born
Posted by Gerard Bain in categories: biological, climatology, life extension, sustainability

SENS Research Foundation co-founder Aubrey de Grey believes in a world in which we no longer age. At a London event, he explained that he believes the first person who will live to be 1,000 has already been born, and we’ll solve this “aging problem” within 20 years.
Aging has plagued biological organisms since life first began on planet Earth and it’s an accepted and universally understood part of life. Sure, things like climate change pose significant threats to society, but aging will almost certainly still exist even if we ever manage to stop damaging our environment.
Nov 15, 2017
A New Futuristic Robot Lets Your Arms Lift Half a Ton
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: biological, climatology, cyborgs, Elon Musk, robotics/AI, space travel, sustainability
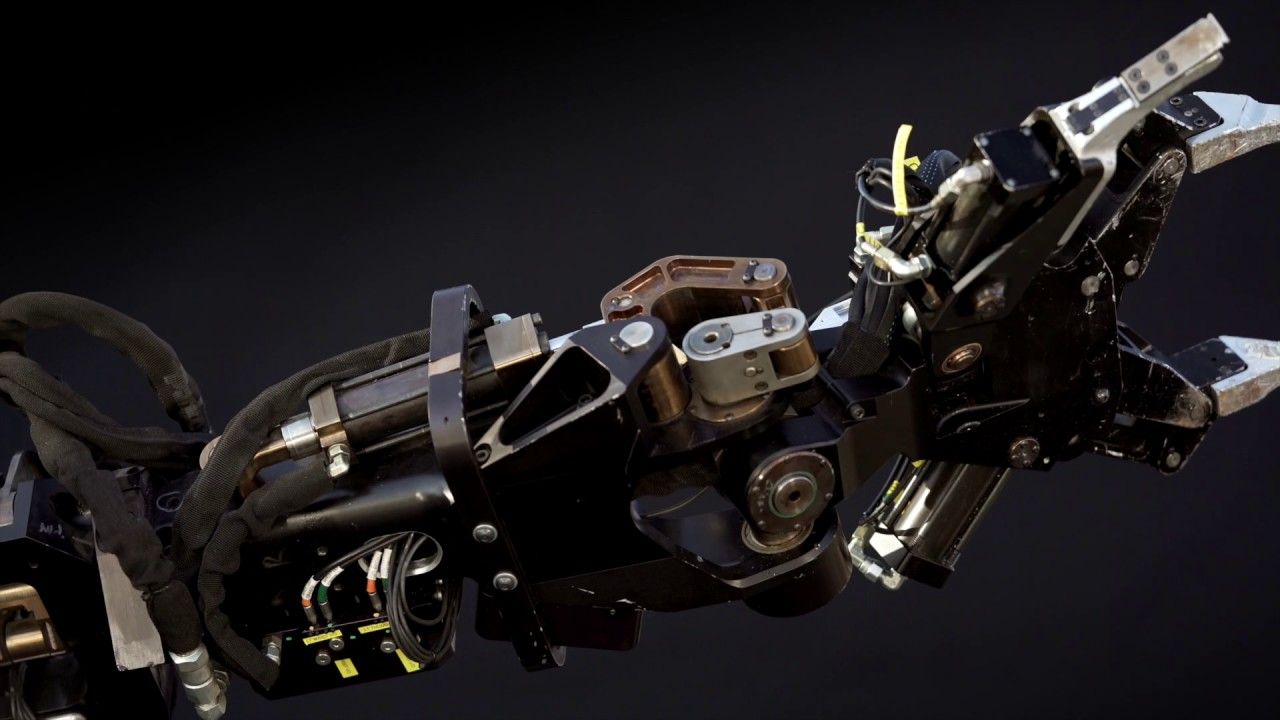

Have you ever lifted half a ton? With the Guardian GT, a set of robotic arms, you could do so with as little as two kilogram (five pounds) of force, allowing you to have superhuman strength.
Elon Musk recently made headlines asserting that, in order for us to both progress and survive as a species, we must merge with machines and become cyborgs. And, as climate change rages onwards and the biological difficulties of completing a human mission to Mars become ever more apparent, many are beginning to agree.
Nov 11, 2017
Scientists decipher mechanisms in cells for extending human longevity
Posted by Anderson Tan in categories: biological, computing, engineering, life extension


A team of scientists at the University of California San Diego led by biologist Nan Hao have combined engineering, computer science, and biology technologies to decode the molecular processes in cells that influence aging.
Continue reading “Scientists decipher mechanisms in cells for extending human longevity” »
Nov 4, 2017
Falling Walls: The Past, Present and Future of Artificial Intelligence
Posted by Derick Lee in categories: biological, robotics/AI
Editor’s Note: The Falling Walls Conference is an annual, global gathering of forward thinking individuals from 80 countries organized by the Falling Walls Foundation. Each year, on November 9—the anniversary of the fall of the Berlin Wall—20 of the world’s leading scientists are invited to Berlin to present their current breakthrough research. The aim of the conference is to address two questions: Which will be the next walls to fall? And how will that change our lives? The author of the following essay is speaking at this year’s Falling Walls gathering.
This is more than just another industrial revolution—it is something that transcends humankind and even biology.
- By Jurgen Schmidhuber on November 2, 2017
Oct 20, 2017
Synthetic Biology and Evolution
Posted by Klaus Baldauf in categories: bioengineering, biological, evolution
Darwinian evolution is old-fashioned. Bioengineering raises new principles for the creation of life but, to what extent can we dispense with the past of our biology.
Oct 16, 2017
Inspired by Octopus Skin, Engineers Develop a Programmable “Camouflaging” Material
Posted by Carse Peel in categories: biological, materials
WOODS HOLE, Mass.—For the octopus and cuttlefish, instantaneously changing their skin color and pattern to disappear into the environment is just part of their camouflage prowess. These animals can also swiftly and reversibly morph their skin into a textured, 3D surface, giving the animal a ragged outline that mimics seaweed, coral, or other objects it detects and uses for camouflage.
This week, engineers at Cornell University report on their invention of stretchable surfaces with programmable 3D texture morphing, a synthetic “camouflaging skin” inspired by studying and modeling the real thing in octopus and cuttlefish. The engineers, along with collaborator and cephalopod biologist Roger Hanlon of the Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL), Woods Hole, report on their controllable soft actuator in the October 13 issue of Science.
Led by James Pikul and Rob Shepherd, the team’s pneumatically activated material takes a cue from the 3D bumps, or papillae, that cephalopods can express in one-fifth of a second for camouflage, and then retract to swim away with minimal hydrodynamic drag. (See video below of live Octopus rebescens expressing its skin papillae.)
Oct 12, 2017
Food From Electricity project bears its first protein-rich “fruit”
Posted by Klaus Baldauf in categories: biological, food
A Finnish research project has created a batch of single-cell protein using just electricity, water, carbon dioxide and microbes, in a small portable lab. While we’re hesitant to call it “food” in its current state, the stuff is edible and nutritious enough to be used for cooking or livestock feed, and the team hopes that the system can eventually be used to grow food in areas where it’s needed the most.