Archive for the ‘3D printing’ category: Page 69
Jan 25, 2019
Studio Roosegaarde wants to turn space waste into shooting stars and 3D-printed housing
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: 3D printing, habitats, space
Have you ever thought about all of the pollution in space? Check out this innovative idea to turn space waste into eco-friendly fireworks and 3D-printed homes.
Jan 23, 2019
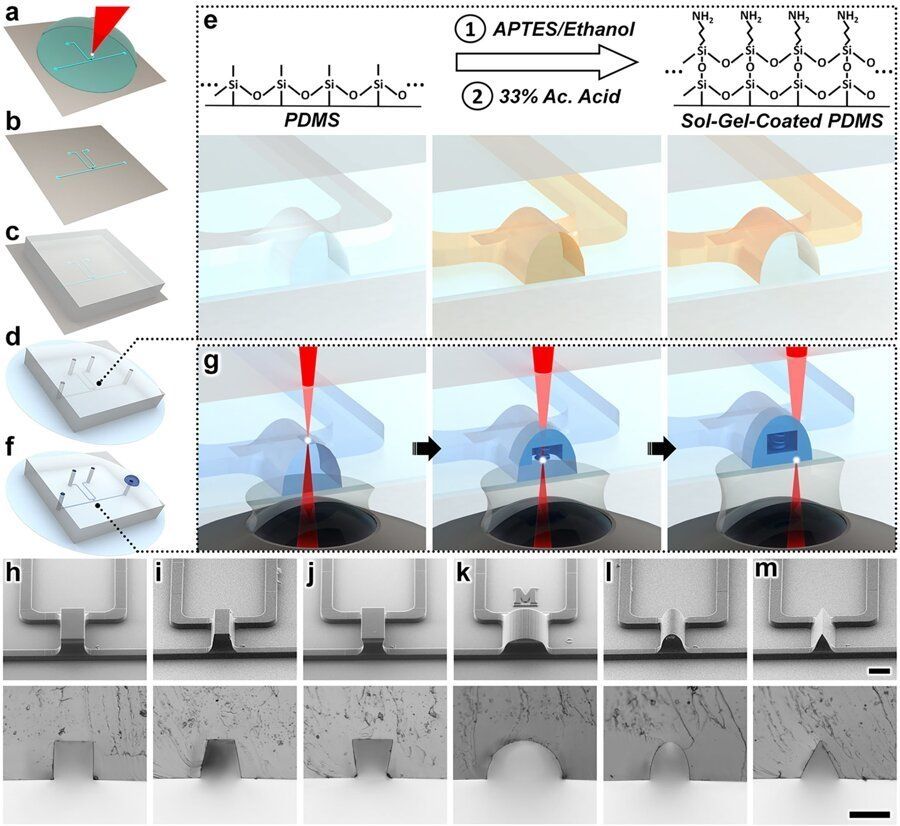
New 3D nanoprinting strategy opens door to revolution in medicine, robotics
Posted by Paul Battista in categories: 3D printing, biotech/medical, robotics/AI
Engineers at the University of Maryland (UMD) have created the first 3D-printed fluid circuit element so tiny that 10 could rest on the width of a human hair. The diode ensures fluids move in only a single direction—a critical feature for products like implantable devices that release therapies directly into the body.
Jan 23, 2019
Aether and UCL Researchers Democratizing 3D Printed Nanotech at 2% of Competitor Cost
Posted by Klaus Baldauf in categories: 3D printing, nanotechnology
Aether collaborating with University College London and Loughborough University to develop 3D printing nanotechnology at a revolutionary low cost.
Erin Abbott erin@discoveraether.com
Jan 22, 2019
Mechanical engineers develop process to 3D print piezoelectric materials
Posted by Paul Battista in categories: 3D printing, mobile phones
The piezoelectric materials that inhabit everything from our cell phones to musical greeting cards may be getting an upgrade thanks to work discussed in the journal Nature Materials released online Jan 21.
Jan 19, 2019
Experimenting with Cancer Treatments Outside the Human Body
Posted by Jeffrey L. Lee in categories: 3D printing, biotech/medical
New research from MIT has resulted in a microfluidic device, the tumor analysis platform (TAP), that can simulate different cancer treatments on biopsied tumor tissue. The TAP device can be 3D printed within one hour and is slightly larger than a quarter. Three cylindrical shafts rise from the surface of the device and serve as ports to input and drain fluids, as well as remove air bubbles. Fluid—including various media, fluorescent markers, or lymphocytes—gets injected into an inlet port adjacent to the trap. The fluid enters through the inlet port and flows past the trap.
A new 3D-printed device from MIT researchers allows for the testing of different cancer treatments on live tumor tissue outside the human body.
Jan 15, 2019
New ultra-fast 3D printing technology uses resin and light
Posted by Genevieve Klien in category: 3D printing

Researchers with the University of Michigan have developed a new 3D printing technology that is capable of printing 100 times faster than normal 3D printers. Unlike traditional 3D printers, which work by applying plastic down as layers, the new technology involves resin that is solidified upward at rapid speeds. The new method is capable of producing complex objects at speeds that traditional printers can’t compete with.
Jan 15, 2019
Paralyzed rats walk again after scientists 3D-print a new spinal cord: Implant successfully fueled nerve growth — and could be a game changer for humans
Posted by Paul Gonçalves in categories: 3D printing, biotech/medical, neuroscience
For the first time, scientists have used rapid 3D printing technologies to create a spinal cord. The team at UC San Diego then put neural cells in it and implanted it into rats, who walked again.
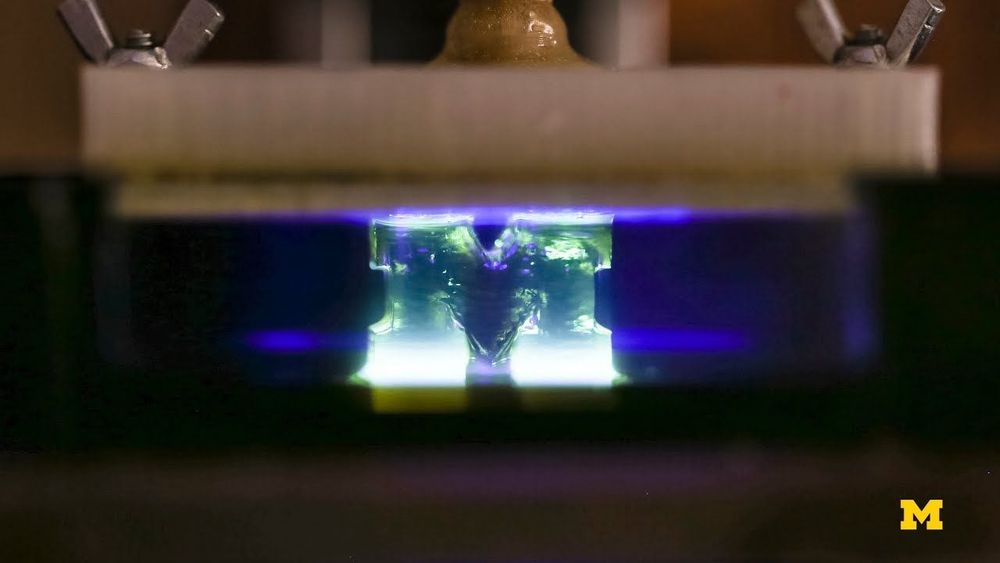
Jan 14, 2019
Researchers Discover a Way to Make 3D Printing 100 Times Faster
Posted by Genevieve Klien in category: 3D printing
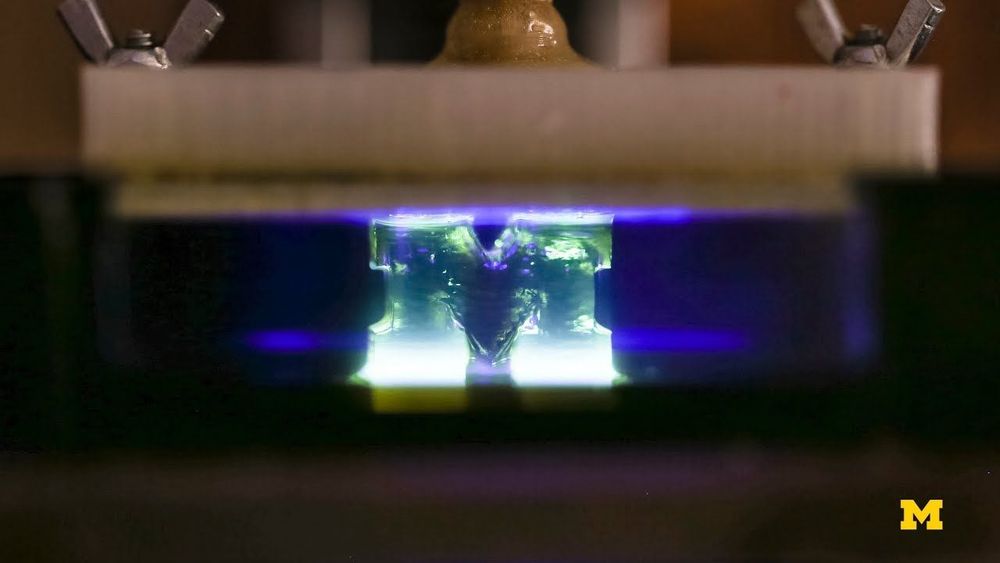

Researchers at the University of Michigan have invented a new method of 3D printing which is up to 100 times faster than conventional existing 3D-printing processes. Here’s how it works, and why it could prove a game-changer for the way that 3D printing is currently used.
Jan 14, 2019
Bio-Printers Are Churning out Living Fixes to Broken Spines
Posted by Klaus Baldauf in categories: 3D printing, bioprinting
A new study shows that 3D-printing a section of spinal cord, living cells and all, restored movement in injured rats.