Jul 24, 2024
Quantum Advantage Challenged: IBM And IonQ Develop Faster Classical Simulation Algorithm
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: computing, information science, quantum physics
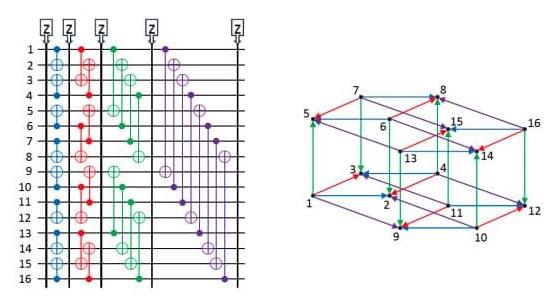
The quantum advantage, a key goal in quantum computation, is achieved when a quantum computer’s computational capability surpasses classical means. A recent study introduced a type of Instantaneous Quantum Polynomial-Time (IQP) computation, which was challenged by IBM Quantum and IonQ researchers who developed a faster classical simulation algorithm. IQP circuits are beneficial due to their simplicity and moderate hardware requirements, but they also allow for classical simulation. The IQP circuit, known as the HarvardQuEra circuit, is built over n 3m 32k inputs. There are two types of simulation for quantum computations: noiseless weak/direct and noisy.
The quantum advantage is a key goal for the quantum computation community. It is achieved when a quantum computer’s computational capability becomes so complex that it cannot be reproduced by classical means. This ongoing negotiation between classical simulations and quantum computational experiments is a significant focus in the field.
A recent publication by Bluvstein et al. introduced a type of Instantaneous Quantum Polynomial-Time (IQP) computation, complemented by a 48-qubit logical experimental demonstration using quantum hardware. The authors projected the simulation time to grow rapidly with the number of CNOT layers added. However, researchers from IBM Quantum and IonQ reported a classical simulation algorithm that computes an amplitude for the 48-qubit computation in only 0.00257947 seconds, which is roughly 103 times faster than that reported by the original authors. This algorithm is not subject to a significant decline in performance due to the additional CNOT layers.