America PAC was created to support these key values: Secure Borders, Safe Cities, Sensible spending, Fair Justice System, Free Speech, Right to Self-Protection.
Page 275
Oct 6, 2024
Astronomers Find Cosmic Filaments Rotate Across Hundreds of Millions of Light-Years
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: computing, cosmology, neuroscience, quantum physics

Scientists have discovered that cosmic filaments, the largest known structures in the universe, are rotating. These massive, twisting filaments of dark matter and galaxies stretch across hundreds of millions of light-years and play a crucial role in channeling matter to galaxy clusters. The finding challenges existing theories, as it was previously believed that rotation could not occur on such large scales. The research was confirmed through both computer simulations and real-world data, and it opens up new questions about how these giant structures acquire their spin.
After reading the article, a Reddit user named Kane gained more than 100 upvotes with this comment: “What if galaxy clusters are like neuron and glial clusters in a brain. And dark matter is basically the equivalent of a synapse. It connects galaxies and matter together and is responsible for sending quantum information back and forth like a signal chain.”
Oct 6, 2024
The Proton Radius Riddle — And an Intriguing Coincidence
Posted by Dan Breeden in category: media & arts
Enjoy the videos and music you love, upload original content, and share it all with friends, family, and the world on YouTube.
Oct 6, 2024
Sabine Hossenfelder, physicist: ‘If you trust the mathematics, we are immortal’
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: life extension, mathematics
The German scientist argues that information cannot be destroyed and, in principle, it is possible that a higher being, one day, in some way, could reassemble it and bring it back to life.
Oct 6, 2024
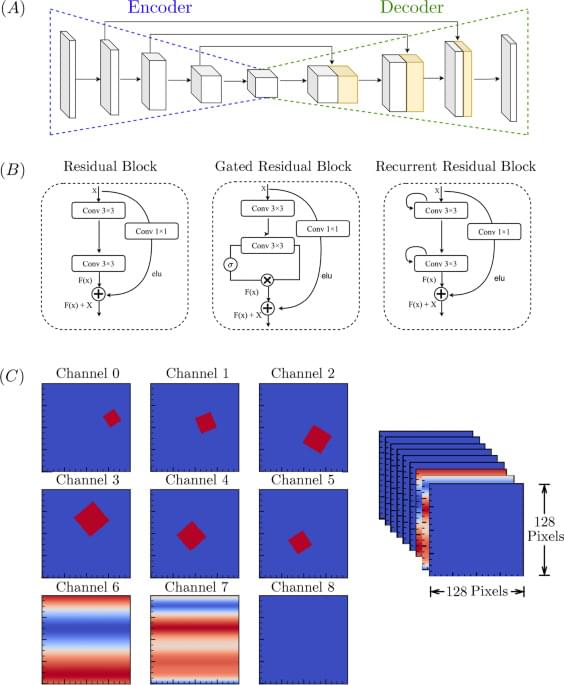
A scalable convolutional neural network approach to fluid flow prediction in complex environments
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: chemistry, climatology, robotics/AI
While machine learning methods can be used for accurate flow prediction in complex environments, such as for urban structures30 or turbulent fields31, generalizing these approaches to domains of arbitrary size and complexity remains a challenging problem. One reason is that flows near and around obstacles depend on factors associated with the fluid (i.e., Reynolds number) or domain (i.e., boundary conditions), and fixing either of these conditions puts bounds on the validity of the estimated fields. Thus, if we seek broad applicability, then we should seek the fewest set of model restrictions that together provide the most accurate flow predictions. To this end, our approach has been to deconstruct certain types of domains into individual obstacles that each maintain some level of geometrical similarity, so that a single neural network model can be used to predict flows near all structural boundaries of the domain. Flows between these structural surfaces, at a scale on the order of the obstacle diameter, are predicted using a second neural network model in series with the first. Together, this serial-modeling approach allows for rapid prediction of flows in domains that can be represented by a disjoint set of structural elements. This type of domain is common, for example, in urban and periurban areas, wherein buildings conform to a common structural motif that affects ground-level velocity fields.
Another relevant length scale is the grid size used to digitize individual domains for read-in by the model. Thus, we investigated how flow patterns can be affected when this input resolution is varied. Although our choice of grid size is somewhat arbitrary, it is dense enough to capture variation in the relevant velocity fields near individual obstacles, but not so dense that producing a large enough cohort of CFD-generated training datasets becomes computationally intractable.
Our approach can also be trained to predict flows with a variable inlet velocity, which, in the case of urban wind flow prediction, permits model parameterization in terms of current meteorological conditions. In the specific case of aerial dispersion of chemicals throughout an urban environment, our predicted flows are considered as the advective field of a drift-diffusion model of molecular dispersion. This advection field plays a central role because concentration fluctuations decorrelate in relationship with the velocity fluctuations of the advection field, and spatial heterogeneity in the flow patterns is determined by the sequence of obstacles in the flow path.
Oct 6, 2024
Scientists Made a Breakthrough Using CRISPR for Autoimmune Diseases
Posted by Paul Battista in categories: biotech/medical, innovation
According to the National Institute of Environmental Health Services, nearly 50 million Americans are currently living with an autoimmune condition. It’s the third-largest category of diseases affecting the nation, according to the agency. Doctors and scientists have been using a number of promising CRISPR treatments to address some of these conditions; now, the results of a new study in China could offer a way to make these treatments even more widely available.
As Nature‘s Smriti Mallapaty explains, the study focused on three people whose treatments were created using donor cells as opposed to cells taken from the patients themselves. This is significant because the prospect of using donor cells allows for CRISPR treatments to be developed in larger quantities — something that could make a big difference in a lot of people’s lives around the world.
Mallapaty describes the three patients in the study as having “severe autoimmune conditions.” One of them, a man in his fifties with systemic sclerosis, said that he started feeling better within a few days, and was able to resume working two weeks after the treatment. This particular study isn’t the only one of its kind — Nature‘s reporting mentions that another trial was subsequently conducted with more patients, while another doctor is leading a similar study using donor cells to treat lupus.
Oct 6, 2024
OpenAI released its advanced voice mode to more people. Here’s how to get it
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in category: robotics/AI

The company says the updated version responds to your emotions and tone of voice and allows you to interrupt it midsentence.
Oct 6, 2024
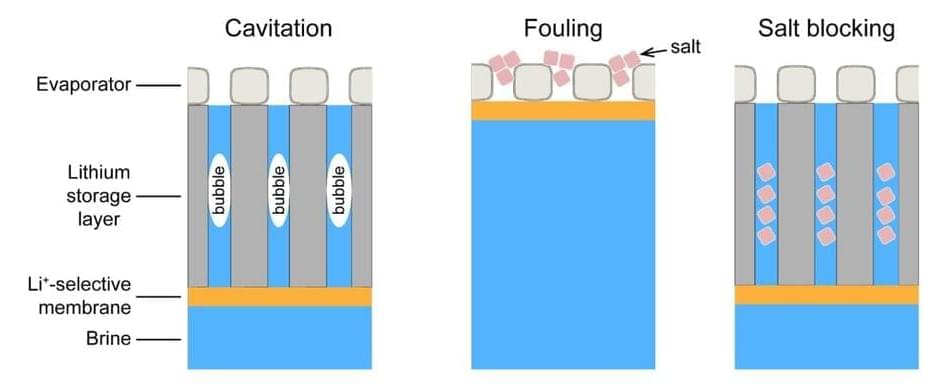
Engineers develop solar-powered lithium extraction from brine
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in category: sustainability
A team of engineers at Nanjing University, working with a pair of colleagues from the University of California, Berkeley, has developed a new way to extract lithium from briny water.
In their paper published in the journal Science, the team describes the process they developed and the device they built and how it could be used to extract lithium from various natural sources. Seth Darling, with Argonne National Laboratory in the U.S., has published a Perspective piece in the same journal issue outlining the work done by the team on this new effort.
Lithium is in high demand due to its use in batteries. Unfortunately, its traditional sources, hard rock ores, are expected to decline in the coming years. Because of that, scientists have been looking for other sources like briny water found in the world’s oceans. Prior research has suggested there is more than enough to meet global demand for as long as needed.
Oct 6, 2024
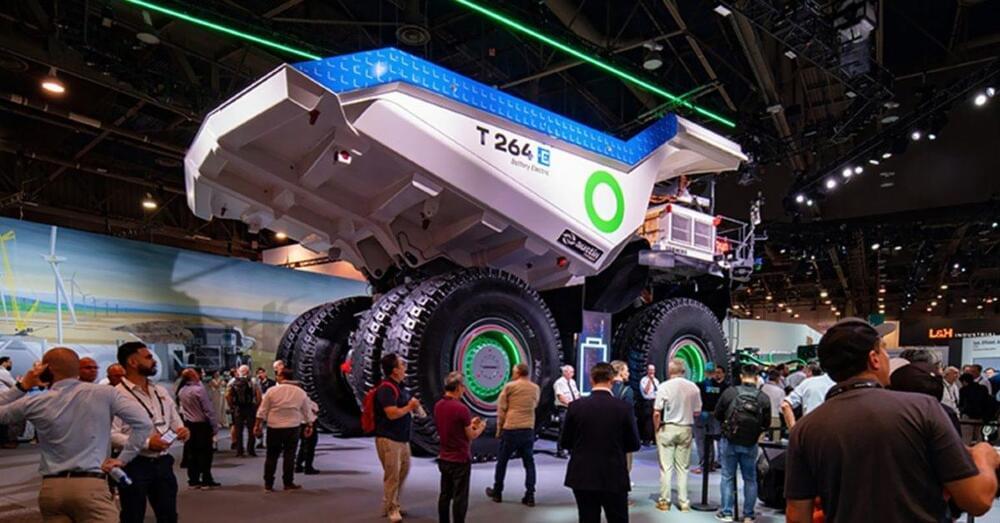
Lightning fast charger: Fortescue 6 MW DCFC for electric heavy equipment
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in category: transportation
Fortescue has an all-new 6 MW DC fast charger that can charge a massive 230 ton haul truck’s 1,900 kWh battery in less than thirty minutes!
Oct 6, 2024
P-Cresyl And Indoxyl Sulfates Are Gut Bacteria-Derived Metabolites That May Be Bad For Longevity
Posted by Mike Lustgarten in categories: life extension, media & arts
Enjoy the videos and music you love, upload original content, and share it all with friends, family, and the world on YouTube.