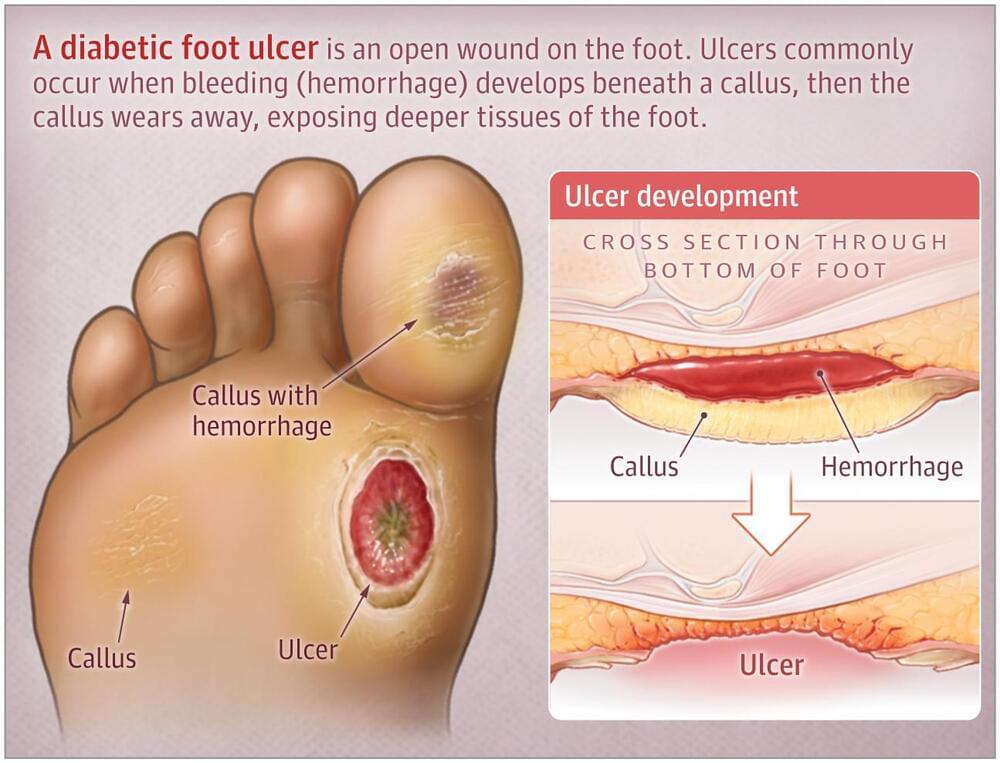
With a mobile app powered by artificial intelligence (AI), Caitlin Hicks, MD, MS, reviews selfies of patients’ feet in real time to track their wounds as part of a clinical trial. The app saves time for Hicks, a vascular surgeon at Johns Hopkins Medicine, but also reduces clinic trips for her patients with diabetes in inner-city Baltimore, many of whom are elderly and less mobile or have other socioeconomic barriers to care. Hicks knows that for these patients, wound vigilance is the linchpin to preventing infection, hospitalization, or, worse, amputation or even death.
Despite their crushing toll, diabetic foot infections remain stubbornly hard to treat, but multidisciplinary care teams, new drugs and devices on the horizon, and practical solutions to socioeconomic factors could budge the needle.